Food Hygiene & Safety
What is the Temperature Danger Zone for Food? Graphical Chart Included
Temperature control plays a crucial role in the preparation and preservation of food. The correct temperature while cooking and storing food ensures both quality and safety. While heat kills bacteria, cold temperatures slow down the growth of bacteria preventing it from reaching harmful levels.
There is a certain temperature range in which harmful bacteria spreads rapidly which is termed as the food temperature danger zone. Suppose you are involved in food handling or preparation. In that case, it is your responsibility to keep foods out of the danger zone by using appropriate heating methods, chilling and storing foods.
Let’s explore what is the temperature danger zone for food, how to keep food out of the danger zone, the right temperature for cooking, reheating, freezing and many more from this blog.
Table of Content
What is the effect of Temperature on Food Safety?
To slow down microbial growth, you should store food at lower temperatures and cook it at higher temperatures. Cooking food above 60°C can kill microorganisms. To ensure food safety, you should be cautious about the food cooking and preservation temperature.
What is the Temperature Danger Zone for Food?
The temperature danger zone for food means the temperature range where food is prone to growing harmful bacteria. Food that is in the danger zone allows foodborne pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli to grow and if consumed, can cause illness to those who consume it and also to those who handle it.
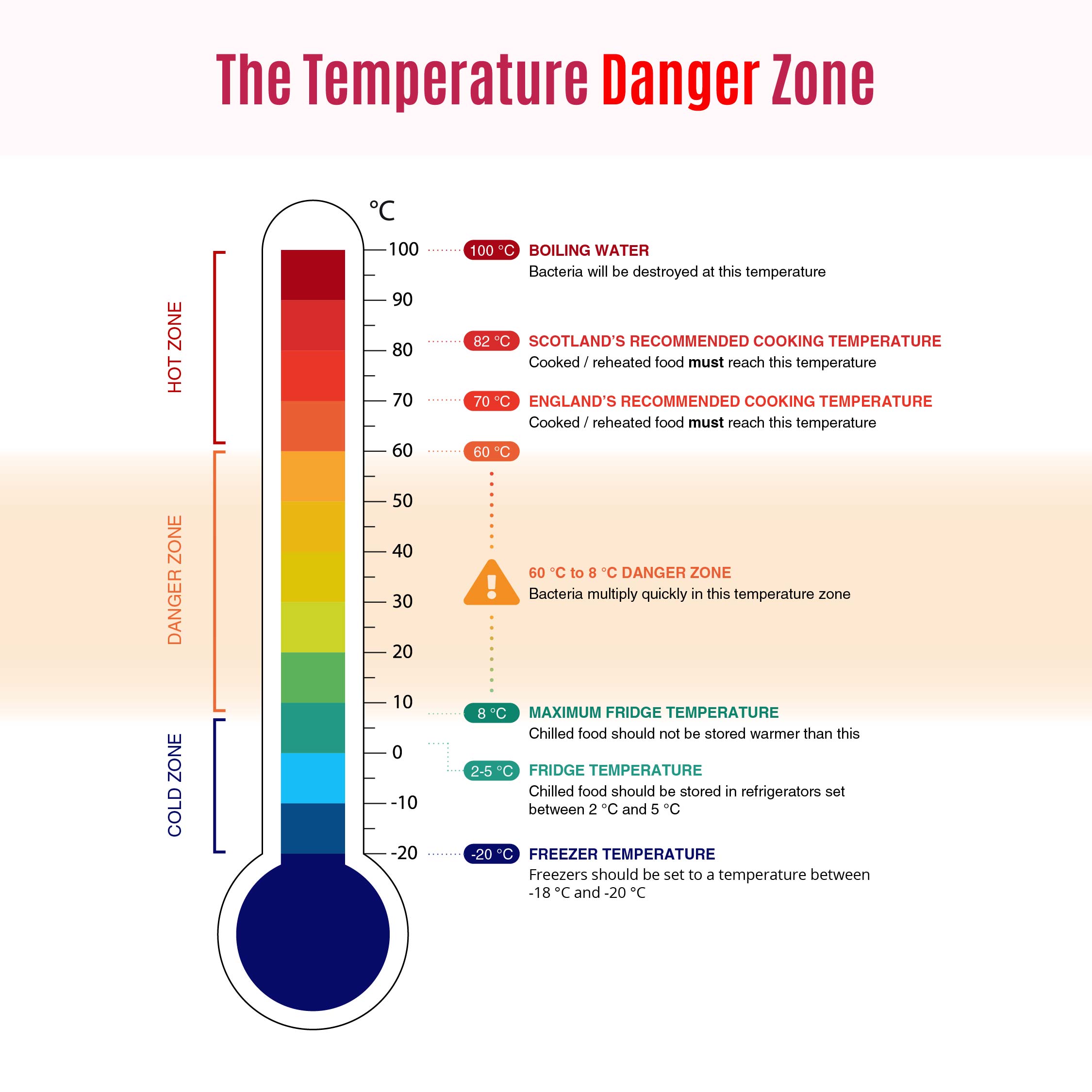
The temperature danger zone for food is between 8°C and 60°C as set by the Food Standards Agency (FSA). This means, bacteria can double in number within this temperature range.
How Long Food can Stay in the Temperature Danger Zone?
The ready-to-eat foods can stay for 4 hours maximum in the temperature danger zone. You should throw the food after 4 hours. Within these 4 hours, you can consume food, chill or reheat it to bring them back to safe temperatures.
What is the Bacteria Danger Zone?
There are certain foods on which bacteria grow at full tilt. The most common types of bacteria that contaminate food are-
- Salmonella – It is most commonly found in milk, raw eggs, dairy products and raw and undercooked meats.
- Campylobacter – Campylobacter is present in unpasteurised milk. Reportedly, 76% of supermarket chickens and 6% of the exterior of supermarket chicken packaging contains this type of bacteria.
- Listeria – Most of the pre-packaged foods contain listeria, such as cooked meats and sandwiches.
As mentioned above the food poisoning bacteria will multiply rapidly in which temperature range (8°C–60°C), the optimum temperature for bacterial growth is 37°C. Under the right circumstances and type of food, bacteria can continue to double in amount every 20 minutes.

Level 2 Food Hygiene and Safety Course for Retail
Standard Temperature for Food
Since the FSA has marked the temperature between 8°C and 60°C to be the danger zone for food, that means food remains safe when it is either chilled or frozen below 8°C or heated above 60°C.
Bacteria breed rapidly when it is warm; it multiplies the quickest between 20 °C and 50 °C. That is why the FSA recommends cooking or heating food thoroughly to 70 °C. At 60°C, the growth of bacteria slows down and above 60°C the bacteria begin to die.
The ideal temperature for chilled food items is below 5 °C. However, freezing food does not eliminate bacteria. Therefore one should cook any defrosted food to ensure that it is safe to eat.
The Process to keep Food out of the Danger Zone
Knowing the correct temperatures for cooking, storing and defrosting food will help you understand the ways to keep food outside the danger zone. As mentioned above, the danger zone for bacterial growth is the temperature between 8°C and 60°C and so, the food safety officers and government regulators have put measures to ensure the food that is for public consumption remains outside the danger zone.
In addition, you need to be concerned about the following to avoid bacteria contamination of food-
Reheating Food
You should not keep the leftover food for more than two hours outside the fridge. However, it would not be safe to leave the food out for more than an hour if the temperature is above 33°C.
Further, You should reheat any leftovers to a minimum internal temperature of 75°C before consumption. Try to consume your fridge leftovers within two days and if you are taking the leftovers from the freezer, eat within 24 hours.
You shouldn’t be reheating the leftovers more than once. While reheating, make sure that your food reaches and maintains the temperature of 70°C or above for two minutes.
Defrosting Food
Foods that are not defrosted properly can cause harmful bacteria to grow, increasing the risk of foodborne diseases. Frozen foods like vegetables and ready meals can be cooked straight from the frozen state without defrosting first. But foods like chicken, beef and fish must be completely defrosted before cooking.
You can reduce the risk of food poisoning by defrosting food using one of these methods-
- Cold water
- Refrigerator
- Microwave
As per Forbes, “You should never thaw food on the counter since harmful foodborne pathogens multiply rapidly when foods are in the danger zone between 40-140°F. It is recommended to always thaw foods in a refrigerator, cold water or a microwave.”
Chilling Food
To ensure food safety, they should be either frozen, chilled or heated to the recommended temperature. Food with an expiry date, cooked dishes and dairy products need to be stored at a temperature of 5°C or below in the fridge.
Before cooking, chilled or frozen food should be kept out for the shortest time possible. After cooking, cool the food for one to two hours at maximum before putting it in the fridge.
Some frozen goods, such as ice cream, remain frozen and do not require any further processing before consumption. You just need to keep it in its frozen state for it to be safe. For other types of frozen food, you must follow the manufacturer’s guidance. Some foods are safe to be cooked instantly from frozen state, which reduces the time the food remains in the danger zone.
What should be the Cooking Temperature for Food?
Cooking food at the correct temperature kills food-borne pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. The Food Standards Agency (FSA) in the UK recommends that the food should be cooked at a temperature of 70°C. For Scotland, the temperature recommendation is 82°C.
It is also important to note how long the food remains at the correct temperature. The FSA suggests that food cooked at a temperature of 60°C must remain at that temperature for 45 minutes, which might not be practical in many circumstances. Food that is cooked to a temperature of 65°C needs to remain at that temperature for 10 minutes. Food needs to remain for 2 minutes at a temperature of 70°C.
If food is cooked to a temperature of 75°C, it needs to remain at that temperature for 30 seconds, and food cooked at a temperature of 80°C needs to remain at that temperature for only 6 seconds!
Top Courses of this Category
How to Check the Food Temperature?
Using a probe thermometer is the best way to check the temperature of cooked or heated food. When using a probe thermometer, insert its metal stem into the middle of the dish. If the stem touches the base of the pan near the heat source, this will give an incorrect reading. When you use your probe, the temperature on the display screen increases rapidly. Record the time the temperature stays above or at the recommended temperature.
There are other ways of checking the temperature as well. For instance, the chicken will turn from pink to white when cooked, and minced beef will turn red to brown. You can also notice the texture of the food changes in baked potatoes, which become soft when cooked.
For frozen and chilled temperatures, you can either use a probe thermometer, a thermocouple, or even an infrared thermometer. The best way to measure the temperature of chilled items is to monitor the temperature of the unit they are stored in. Most commercial fridges and freezers have an electronic thermometer built-in and displayed. For domestic fridges and freezers, you can buy a temperature gauge and leave it in the unit. This way, you can ensure that your food is always at the correct temperature.
Food Temperature Danger Zone Chart
The chart illustrating the temperature ranges that are safe and hazardous for food safety is the Food Temperature Danger Zone Chart. Have a close look at the image to identify the temperature perfect to kill the bacteria present in food.
Conclusion
Foodborne diseases like E. coli and Hepatitis A might take a heavy toll on you if you consume food kept at room temperature for a long period of time. Whether you work in a professional kitchen or manage the household kitchen, make sure you keep food out of the temperature danger zone.
Lastly, this blog lets you learn how to design your kitchen that adheres to food safety rules and guidelines. Don’t forget to check it!
FAQ
What is the danger zone for food?
The Food Standards Agency (FSA) defines the danger zone in food temperature as 8°C to 60°C. Below this temperature, your food should remain good for consumption for a few days, depending on the dish.
What are 5 food safety rules?
- Maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
- Separate raw and cooked foods to avoid cross contamination.
- Cook at safe temperatures and make sure your food is thoroughly cooked.
- Store food at safe temperatures.
- Always use clean, safe water.
What temperature does salmonella grow?
Ideally, Salmonella grows at a temperature between 6-46°C.
What temperature are most bacteria killed at?
The optimum temperature for bacterial growth on food is between 40 and 140 degrees Celsius. This is the danger zone temperature in cooking and also the danger zone of food storage. If you prepare food at temperatures between 140 and 165 degrees Celsius. They cannot survive temperatures exceeding 212 degrees Celsius.
What are the 3 types of food contamination?
The majority of food safety dangers that cause food contamination are classified as biological, physical, or chemical contamination.
What is the 24-hour rule?
The rule tells us that food is safe to consume up to 2 hours after being cooked. We can also refrigerate it for later use. If the duration exceeds 2, but not 4 hours, the food is still safe for us to consume but not refrigerate. After 4 hours, the food is no longer safe.
What temperature is too cold for a freezer?
If your freezer stays at or below 0°F (-18°C), your cold food (frozen) should be safe to eat permanently. Keep in mind that if you keep food for an extended period of time, it may develop freezer burn or have a distinct appearance and taste.
Can you eat cooked meat that’s been left out overnight?
No. Food should be thrown if it has been left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
Can you put warm rice in the fridge?
Ideally, it’s best to let the rice cool down to room temperature and then put it in the fridge. But don’t let your rice sit (or any other hot foods) down outside for more than 2 hours, and a typical rice dish won’t take that long to cool either. If you have a feeling that it may take longer, divide the dish into smaller portions.
How long after cooking chicken can you put it in the fridge?
Even if the chicken dish is still warm, you should try to refrigerate it within 2 hours of cooking. Don’t wait for it to cool down further.
What to Read Next:
- Can you Reheat Fish? The Science and Process of Reheating Fish
- What Does Due Diligence Mean in Food Hygiene? Examples of Due Diligence
- What is the Most Common Type of Food Contamination – Physical Contamination
- What does Soy Milk Taste Like – A Guide to Taste, Storage & Usage
- Can You Reheat Risotto? Safety and The Science of Reheating Risotto
- What are High Risk Foods – Top 20 High Risk Foods
- Can You Reheat Prawns? The Science of Reheating Prawns and Shrimps