First Aid
What is Anaphylaxis – Causes & Symptoms
A person’s allergy symptoms can be light or extreme. When you have an allergy, your immune system overreacts to an allergen, releasing chemicals that lead to allergy symptoms. You might be wondering what Anaphylaxis is.
Further, these unwanted symptoms typically affect just one part of the body. However, some people can experience an anaphylactic reaction, which is far more serious. Usually, more than one area of the body is affected together by this reaction.
Table of Content
What is Anaphylaxis?
An allergic reaction that can be extremely serious and even dangerous is called anaphylaxis. The most common anaphylactic reactions are to foods, medicines, latex, insect stings, and foods.
Anaphylaxis requires quick medical attention, including a hospital emergency room trip. It can happen within seconds or minutes of exposure to specific allergens. If not treated immediately, it may cause deadly conditions like shock and other significant consequences affecting different body systems.
Today, we’re taking a look to find out what is anaphylaxis and its remedy.
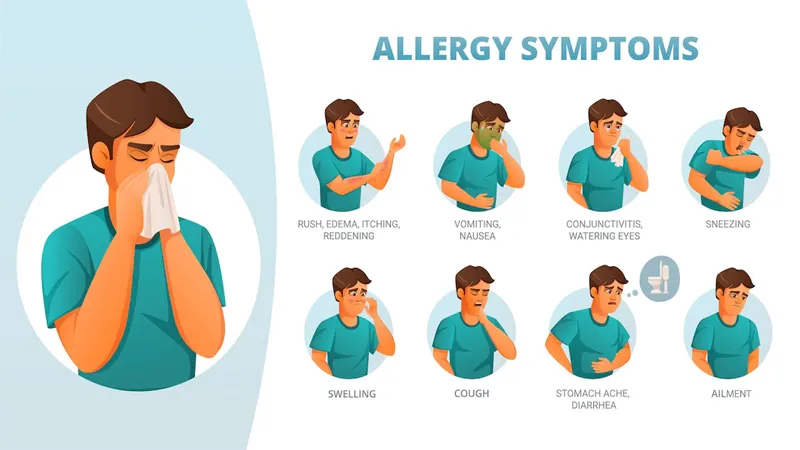
Symptoms of Anaphylaxis
Most people are confused about what is anaphylaxis. Moreover, there are also confutations regarding the term anaphylaxis. We can define anaphylaxis as a severe allergic reaction that can be dangerous. Exposure to an allergen, like peanuts or bee stings, can happen seconds or minutes later.
The anaphylaxis signs and symptoms include:
- feeling faint
- breathing problems, such as fast or weak breathing
- wheezing
- a fast heartbeat
- rough skin
- fear and worry
- becoming unconscious
What to Do If Someone Has Anaphylaxis?
If someone has anaphylaxis, the following actions can be taken:
- If the person has an adrenaline auto-injector, use it, but first, ensure you know how to use it.
- Even if they start to feel better, call 999 for an ambulance right away and let them know you think they are having anaphylaxis.
- If possible, remove any triggers; for example, carefully remove any stingers that may be stuck in the skin.
- If the person has breathing problems and needs to sit up to help them, lay the person down and up their legs. If they are pregnant, place them on their left side.
- Give another injection after 5 minutes if there is no improvement and a second auto-injector is available.
If you feel confident, you can perform these actions on your own if you have an anaphylactic reaction.
Causes of Anaphylaxis
The body’s natural defence system, the immune system, reacts badly to a trigger, resulting in anaphylaxis.
This is often something you’re allergic to, but not always.
Common triggers for anaphylaxis include the following:
- Foods include nuts, milk, seafood, shellfish, eggs, some fruits, and dairy products.
- Medicines, including some antibiotics and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), like aspirin.
- Stings from insects, especially spider and bee stings.
- Contrast agents are colours that are used in some medical exams to make particular body parts stand out more on scanners.
Some condoms and rubber gloves include a type of rubber called latex.
Sometimes there is no obvious trigger. This is known as idiopathic anaphylaxis. Usually, anaphylaxis starts suddenly and soon gets worse. Anaphylactic shock can result from an anaphylactic allergic reaction. When your body gets an anaphylactic shock, your blood pressure suddenly drops and your lungs collapse, effectively stopping regular breathing.

Emergency First Aid at Work (EFAW) Refresher Course
- Accredited Courses
- Tutor Support Included
- 3 Installment Plan at checkout
- 14 Days Money Back Guarantee
Preventing Anaphylaxis
Take steps to avoid similar incidents if you have a serious allergy or have already experienced anaphylaxis.
You can reduce your risk by doing the following:
Identify triggers
You should contact an allergy clinic for tests to find any triggers if you have experienced anaphylaxis but have not yet been given an allergy diagnosis.
The most common tests are:
- A skin prick test
A limited amount of a suspected allergen is prickled onto your skin to check if it reacts.
- A blood test
Your blood is taken to test how it responds to a possible allergy.
Avoid triggers
If a trigger has been found, you must take steps to avoid using it whenever possible. Here are some ideas we have for keeping away from particular triggers.
Food
The risk of coming into contact with a food allergy can be reduced by:
- Checking the ingredients and labels on food.
- Letting a restaurant’s workers know what you’re allergic to so it won’t be present in your meal.
- Keeping in mind that some foods may contain a small number of allergens.
Develop Your Team to Lead The Industry
Get fully accredited thousands of high quality online courses taught by the world’s leading experts suitable to companies of all sizes.
Insect stings
By taking simple safety measures, such as the following, you can lower your risk of being stung by an insect:
- Moving slowly and quietly away from hornets or bees.
- If you spend time outside, especially in the summer, using bug sprays.
Medicines
There are usually safer options if you have an allergy to a particular class of medicine.
For example, if you have an allergy to:
- Penicillin
Usually, taking a different class of antibiotics known as macrolides is safe.
Top Courses of this Category
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Medications (NSAID)
Paracetamol is often safe to take. However, you should carefully review products’ ingredients like cold medicines to ensure they do not contain NSAIDs.
Always let a health professional know if you have any medicine allergies because they might not be aware of them.
FAQ
What causes an anaphylactic reaction?
Bee stings and consuming foods like peanuts or tree nuts are the main causes of most cases.
What is an example of an anaphylactic reaction?
When you have a serious allergic reaction, it is called anaphylaxis. Examples include harmful effects from particular foods or bug bites.
How can you tell if you have anaphylaxis?
Runny nose and skin rashes, common allergy symptoms, could be the earliest signs of an anaphylactic reaction. However, more alarming symptoms start to occur after 30 minutes.
Who is at risk of anaphylaxis?
The risk of having anaphylaxis is highest in people with other allergy problems, such as asthma or atopic eczema.
What are the 4 most common symptoms of anaphylaxis?
The four most common signs of anaphylaxis are skin rashes, low blood pressure, a weak pulse, and dizziness or fainting.
What is the difference between an allergy and anaphylaxis?
In children, allergic reactions are common. Most reactions are minor. On the other hand, anaphylaxis’s most serious type of allergic reaction can be deadly.
How long do anaphylaxis symptoms last?
In rare situations, anaphylaxis may last for several days. Anaphylaxis happens suddenly, typically reaching its intensity in 5 to 30 minutes.
What to do if someone has anaphylaxis?
If you think the person has anaphylaxis, call 999 for an ambulance immediately, even if they start to feel better.
What is anaphylactic shock?
It is a serious, often deadly allergic reaction to an allergen to which the body has developed a greater sensitivity.
Does pollen cause anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis is an uncommon reaction to pollen and other inhaled allergens. Anaphylactic reactions happen to some persons for unknown reasons.
Conclusion
A severe allergic reaction is called anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis can affect a flood of chemicals from the immune system that can put you into shock.
Even if you avoid injuries, you’ll probably come into contact with something you’re allergic to at some point. Fortunately, by being aware of the warning signs and symptoms of an anaphylactic reaction and having a strategy to address those symptoms promptly, you can respond to an allergy emergency quickly and successfully.
I hope this article has helped you understand what is anaphylaxis a little bit better.
What to Read Next:
- How Many First Aiders Do I Need
- What is the Primary Survey First Aid – Primary and Secondary Survey in First Aid
- What does CPR stand for? A Comprehensive Overview
- How Much Does a First Aid Course Cost? Course and Certificate Price